About Iran
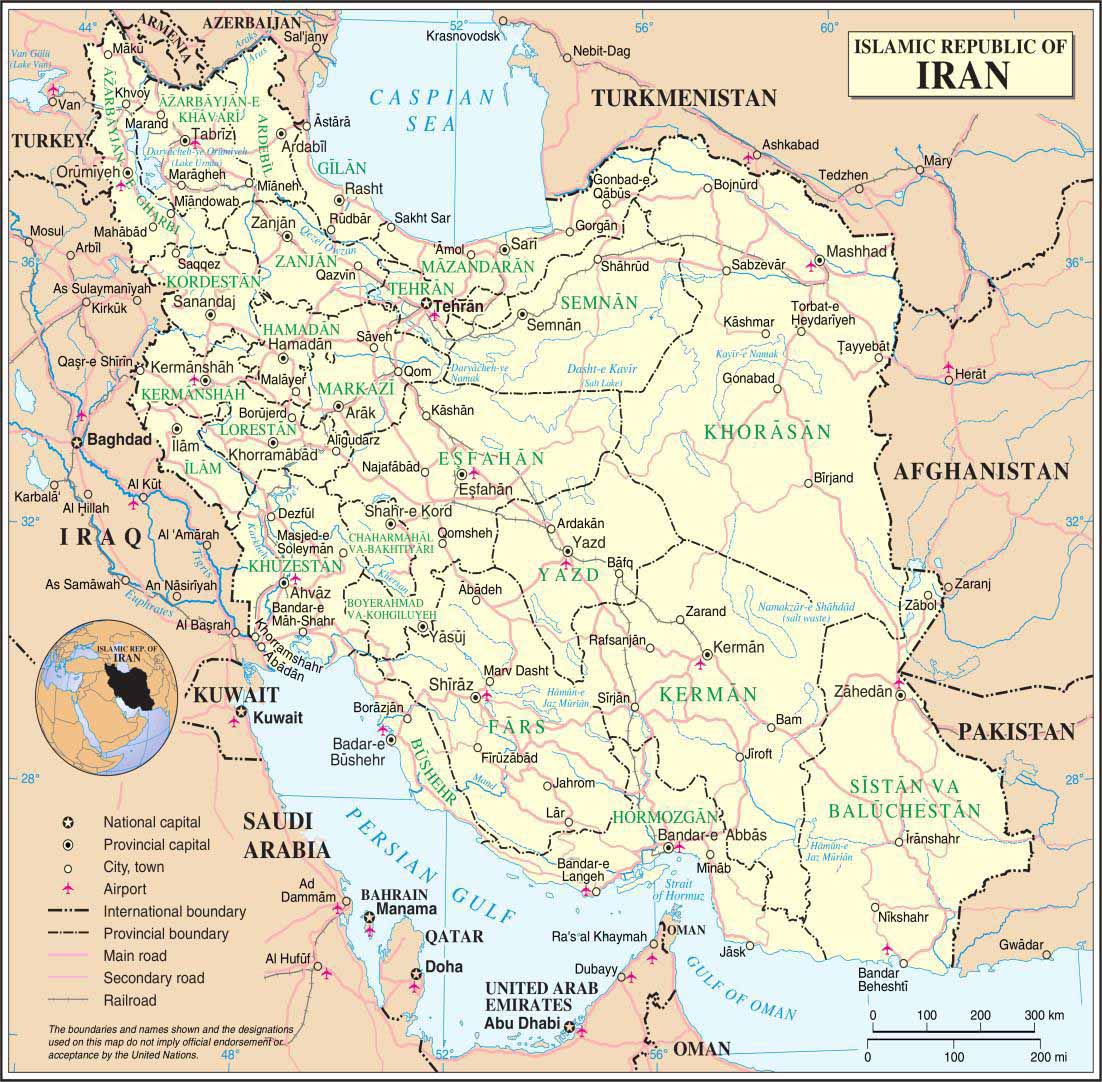
Geography
Iran is the 18th largest country in the world, with an area of 1,648,195 Sq km. Its borders are with Azerbaijan 611 km, with Azerbaijan-Naxcivan exclave, 179 km and Armenia 35 km to the north-west; the Caspian Sea to the north; Turkmenistan 992 km to the North-East; Pakistan 909 km and Afghanistan 936 km to the East; Turkey 499 km and Iraq 1,458 km to the West; and finally the waters of the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the South.
The populous Western part is the most mountainous, with ranges such as the Caucasus, Zagros and Alborz Mountains. The northern part of Iran is covered by dense rain forests called Shomal. The eastern part consists mostly of desert basins such as the Dasht-e Kavir, The only large plains are found along the coast of the Caspian Sea and at the northern end of the Persian Gulf.
Climate
On the northern edge of the country (the Caspian coastal plain) temperatures rarely fall below freezing and the area remains humid for the rest of the year. Summer temperatures rarely exceed 29 °C. To the west, settlements in the Zagros basin experience lower temperatures, severe winters with below zero average daily temperatures and heavy snowfall. The eastern and central basins are arid, with less than 200 mm of rain, and average summer temperatures rarely exceed 38 °C. The coastal plains of the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman in southern Iran have mild winters, and very humid and hot summers.
Regions, Provinces and Cities
Iran is divided into five regions with thirty one provinces (ostān), each governed by an appointed governor (ostāndār). Tehran, Isfahan, Ahvaz, and Qom. Tehran, with a population of 7,705,036, is the largest city in Iran and is the capital.
Mashhad, with a population of 2,410,800, is the second largest Iranian city and the capital of the Razavi Khorasan Province. Mashhad is one of the holiest Shia cities in the world as it is the site of the Imam Reza shrine. It is the centre of tourism in Iran, and between 15 and 20 million pilgrims go to the Imam Reza's shrine every year. Isfahan population 1,583,609, Tabriz population 1,378,935, Karaj population 1,377,450 and Shiraz population 1,214,808 are other major cities of Iran.
Economy
Iran's economy is a mixture of central planning, state ownership of oil and other large enterprises, village agriculture, and small-scale private trading and service ventures. In 2014, GDP was $404.1 billion. Iranian rial, serves as the country's currency.
Iran has leading manufacturing industries in the fields of car-manufacture and transportation, construction materials, home appliances, food and agricultural goods, armaments, pharmaceuticals, information technology, power and petrochemicals. Economic sanctions against Iran have affected the economy and led to a steep fall in the value of the rial. Following a successful implementation of the 2015 nuclear and sanctions relief deal, the economic climate is expected to improve.
Energy
Iran holds 10% of the world's proven oil reserves and 15% of its gas. It is OPEC's second largest exporter and the world's fourth oil producer. Iran has the second largest proved gas reserves in the world after Russia, with 33.6 trillion cubic meters, and third largest natural gas production in the world after Indonesia, and Russia. It also ranks fourth in oil reserves with an estimated 153,600,000,000 barrels.
Rapid industrialization have caused electric power demand to grow by 8% per year which is planned to be met by bringing on line new gas-fired plants and by adding hydroelectric, and nuclear power generating capacity. Iran’s first nuclear power plant at Bushehr went critical in 2011.
Science and Technology
Iran placed its domestically built satellite, Omid into orbit on the 30th anniversary of the 1979 Revolution, on 2 February 2009, through Safir rocket, becoming the ninth country in the world capable of both producing a satellite and sending it into space from a domestically made launcher. The Iranian nuclear program was launched in the 1950s. Iran is the seventh country to produce uranium hexafluoride, and controls the entire nuclear fuel cycle.
Languages
The majority of the population speaks the Persian language (61 %), which is also the official language of the country. Others include the Azerbaijanis (16%) Kurds (10%), Lurs (6%) and rest of the Iranian languages (7%) of the population.
Religion
Historically, Zoroastrianism was the dominant religion in Iran, particularly during the Achaemenid, Parthian and Sassanid empires. This changed after the fall of the Sassanid Empire by the Muslim Conquest of Iran, when Zoroastrianism was gradually replaced with Islam. Iran was predominantly Sunni until the Safavid dynasty forcibly converted the country to Shia Islam in the 16th century. Today, the Twelver Shia Islam is the official state religion, to which about 90% to 95% of the population officially belongs.
India-Iran Relations
Political Relations
India-Iran relations span centuries marked by meaningful interactions. The two countries shared a border till 1947 and share several common features in their language, culture and traditions. Both South Asia and the Persian Gulf have strong commercial, energy, cultural and people-to-people links. The two countries have in place several bilateral consultative mechanisms at various levels which meet regularly. Foreign Offices of both countries also hold regular consultations on bilateral and regional issues
Commercial Relations:
India-Iran enjoys economic and commercial ties covering many sectors. However, the trade relations have traditionally been buoyed by Indian import of Iranian crude oil resulting in overall trade balance in favour of Iran. The India-Iran bilateral trade during the fiscal 2013-14 was USD 15.26 billion. India imported US$ 10.33 billion worth of goods mainly crude oil and exported commodities worth US$ 4.92 billion. India’s export to Iran during the period April- September 2014 stood at USD 2.03 billion. India-Iran bilateral trade for the period April-September, 2014 was USD 7.35 billion, an increase of 15% over the bilateral trade over the same period last year.
India and Iran hold regular bilateral discussions on economic and trade issues within the framework of India-Iran Joint Commission Meeting (JCM). The 17th India- Iran Joint Commission was held in Tehran on May 4, 2013 Mr. Abbas Akhoundi, Minister of Roads and Urban Development of Iran visited India on 25 November, 2014 and met Mr. Nitin Gadkari, Minister of Roads and Transport and Mr. Suresh Prabhu, Minister of Railways.
Cultural Relations:
On 03 May 2013 Shri. Salman Khurshid, Hon’ble External Affairs Minister of India, officially inaugurated the India Cultural Center in Tehran, when he visited Iran for the 17th India-Iran Joint Commission Meeting (JCM).Tehran from 25-28 December, 2014.
Indian community:
The Indian community in Iran, which was sizeable earlier, has dwindled and now it is a small one consisting of about 100 families in Tehran and about 20 in Zahedan. There are a number of Indian students in Iran, approximately 800, a large number of whom pursue theological studies in Qom. There are about 8,000 Iranian students studying in India. India provides 67 scholarships every year to Iranian students under ITEC, ICCR, Colombo Plan and IOR-ARC schemes.
India over the years has emerged as one of the favourite tourist destinations for Iranian tourists and every year around 40,000 Iranians visit India for various purposes. In February 2011, India successfully outsourced the tourist visa collection in Tehran to facilitate the visa services for Iranian tourists visiting India.
Business Potential between INDIA and IRAN
- Considering the present geopolitical situation between India and Iran there is immense scope for cooperation between Iran and India.
- India in one of largest Energy consumption centre while Iran is one the largest exporter of Oil and gas in Middle East. Iran has one of the world’s largest proven reserves of natural gas.
- In recent times due to advent of shale gas in USA and their reduction of energy import needs from middle east and other destination, it is more prudent for Iran to explore and ensure new market like India.
- For India approx 70 % of oil supply is from Middle East (approx 125 Million tons per annum).It is prudent to diversify and increase the supply of oil and gas from countries like Iran.
- Considering long term G-G economic cooperation in various hydrocarbon related projects it can be a win win situation for India as well as Iran.
Size of Indian Market
- 1 Billion plus consumers
- Approx 300 Million Middle class people
- 4th largest economy
- Favoured destination for BPO
- 10th most industrialized country
- Average 5yr Growth Rate of GDP is 7-8%
- FDI US $ 25 billion in 2009-10 from US $ 5 billion in 2003
- 2.0 Trillion USD economy.
Opportunities for India in Iran
Iran Oil Sector
- Import of Oil from Iran on long term basis
- Participation in Iranian upstream sector
- Participation in Iranian Refinery & Petrochemical Sector
- Support for development of Iranian Petrochemical downstream Sector in cludingHuman resource.
Gas Sector
- Import of LNG from Iran on long term basis
- Participation by Indian companies in Iranian LNG Liquifaction facilities (Upstream/midstream)
- Participation of Iranian companies in Indian LNG Import terminals and regasification facilities
Opportunities for Iran in India
India Oil Sector
- Export of Oil to have assured market for long term
- Participation in Indian Refineries and Petrochemical Projects
- Participation in Strategic Oil Storage Facility of ISPRL in India to have assess to nearby South-East Market
Gas Sector
- Export of LNG on long term basis to have market access
- Participation in Indian LNG Storage and Regasification Terminals
- Get human resource trained in Hydrocarbon sector for future development
Infrastructure
- Major thrust areas of Indian Government between 2015-2020.
- Infrastructure projects in roads / highways, railways, ports etc. @ 40 billion $
- Power Plants @ 30 billion $
- Oil & Gas projects @ 20 billion $
- Solar &Wind Energy-160 GW
Opportunities in Other Sectors
Import from Iran
- Fertilizers like Urea, Ammonia
- Rock phosphate
- Bitumen
- Petrochemicals like PVC, HDPE, PP, and LLDPE
- Resins
- Minerals
- Carpets
Export from India
- Export of Commodities, plant equipments and machineries, pipes and other items.
- Participation in EPC, EPMC projects in oil and gas as well other sectors
- Get human resource trained in Hydrocarbon sector for future development


